Home | Research & Resources | Gambia
Key Findings
The prevalence of FGM/C among women aged 15–49 in The Gambia is 75.7%.
44% of women aged 15–49 believe the practice should be continued.
Geography
Basse, the most rural region of the country, has the highest prevalence (95% of women aged 15–49); Banjul, the most urbanised area, has the lowest prevalence (48.8%)
Age
54.8% of women aged 15–49 were cut before the age of 5; 28.1% between the ages of 5 and 9
Type
‘Cut, flesh removed’ is the most common type of FGM/C practised
Agent
95.7% of FGM/C is carried out by ‘traditional circumcisers’
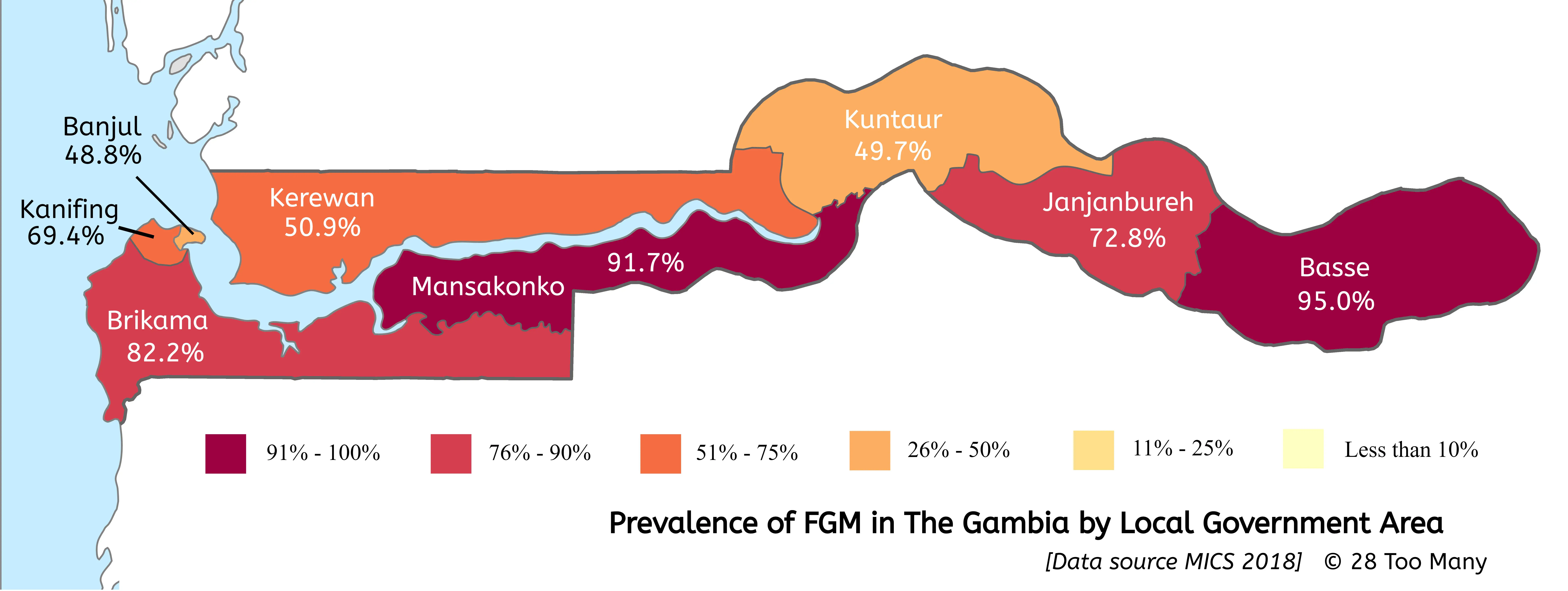
Distribution of FGM/C across The Gambia
FGM/C is practised across all eight Local Government Areas (LGAs) in The Gambia and by both Christians (20.9% of Christian women aged 15–49) and Muslims (77.3%).
The LGA with the highest prevalence is Basse, the eastern-most and most rural region, at 95% of women aged 15–49. The LGA with the lowest prevalence is Banjul, a coastal area and the most urbanised, at 48.8%. The Basse region is predominantly inhabited by the Sarahule, Mandinka and Fula ethnic groups, whereas the coastal areas of Banjul and Kanifing are predominantly inhabited by the Wolof (among whom the prevalence of FGM/C has historically been the lowest among The Gambia’s different ethnic groups) and the Mandinka. Overall, the prevalence of FGM/C among women aged 15–49 who live in urban areas is 77.3%, and among those living in rural areas is 71.7%.
According to the MICS 2018, the overall prevalence among women aged 15–49 is 75.7%. By comparison, the MICS 2010 found that prevalence among women of the same age-range was 76.3%, suggesting that the extent of the practice has remained broadly similar in recent years.
Of women aged 15–49 who have heard of FGM/C, 44% feel that the practice should continue, although among women who have not undergone FGM/C, that figure drops to 6.6%.
Trends in FGM Prevalence in The Gambia
Due to the large age-range (15–49 years) of women included in the MICS surveys, changes in the overall FGM/C prevalence of a country over time may not fully illustrate the progress that has been made. Breaking down the most recent prevalence data by age group can give additional insights into whether the practice is in decline.
In the case of The Gambia, however, the FGM/C prevalence is broadly the same across all age cohorts, suggesting that the extent of the practice has not changed significantly in recent years.
FGM/C Legislation in Gambia
The Women's (Amendment) Act 2015 addressed the issue of harmful practices for the first time in The Gambia by introducing Section 32A (Prohibition of female circumcision) and Section 32B (Accomplices to female circumcision). Very few prosecutions have reportedly taken place since the ban was introduced and case details are limited.
Development Indicators
Population Growth
2,332,091 (as at 17 June 2020), with a 1.87% growth rate (2020 est.)
Infant Mortality
39 deaths per 1,000 live births (2019)
Maternal Mortality
597 deaths per 100,000 live births (2017)
SDG Gender Index
Ranked 118 out of 144 countries with a score of 53.5% (2022)


.webp)
.webp)

_cover.webp)
