Home | Research & Resources | Indonesia
Key Findings
The prevalence of FGM/C among women aged 15–64 in Indonesia is 50.5%.
The term sunat is used to describe FGM/C in Indonesia.
20% experienced WHO types of FGM/C, while 19.3% underwent a symbolic form of the practice.
Due to population size, Indonesia has the highest number of women and girls impacted by FGM/C in the world.
Place
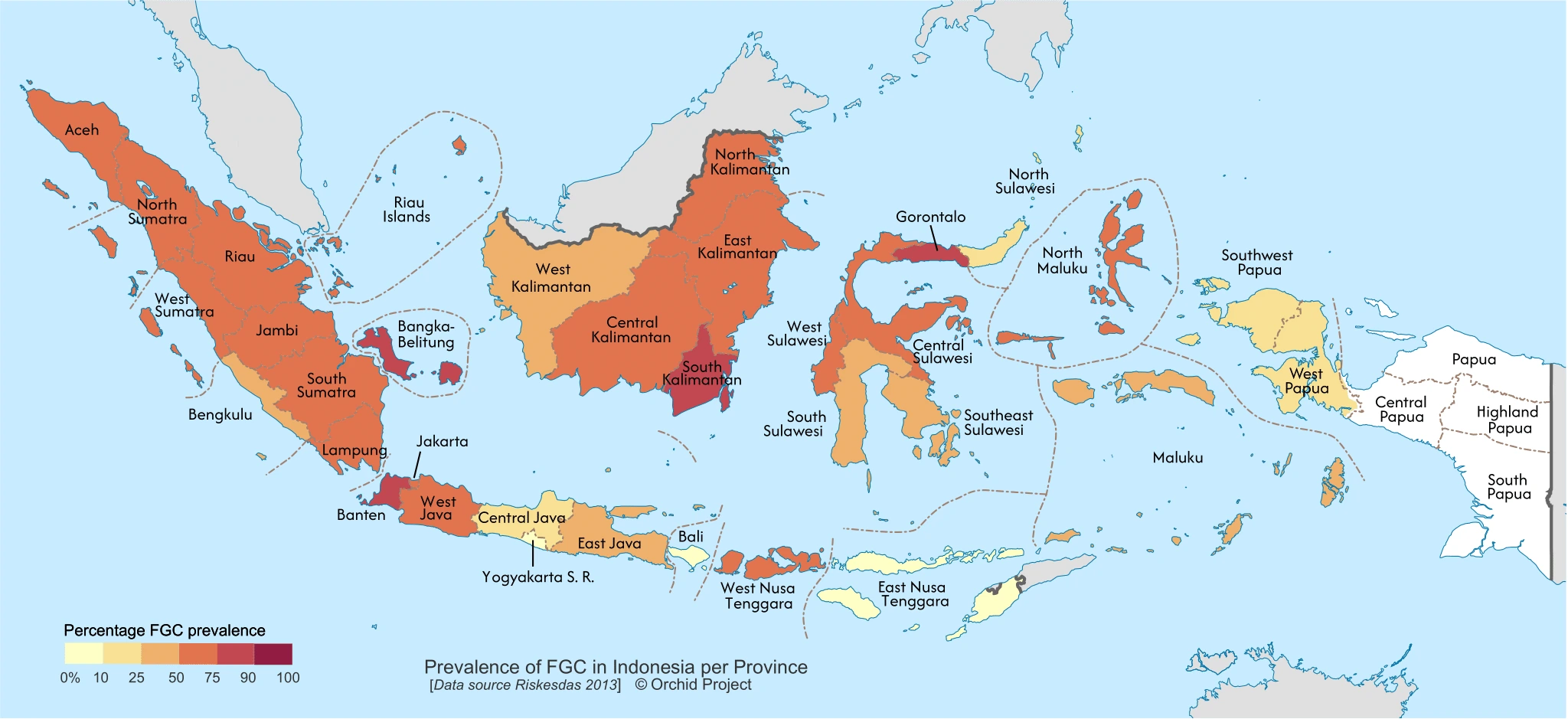
FGC is spread over the whole country, highest on Sulawesi Island (81.2% for all methods of sunat and 50.9% of WHO FGC / unknown), and lowest on Jawa / Bali (38.9% of all methods of sunat and 24.4% of WHO type FGC / unknown).
Age
Nearly 70% of girls undergo sunat before the age of 1 year old, with 26% up to 10 days of their lives.
Type
Type 1 and Type 4 are the most commonly practised in Indonesia. Approximately 4 girls out of 10 have been cut, 4 girls out of 10 have undergone a symbolic practice (without a cut) and 2 out of 10 do not know or remember.
Agent
Girls are cut by midwives, traditional birth attendants or other health professionals.
Distribution of FGM/C across Indonesia
The practice is spread across the country. In 2021, the Ministry of Women’s Empowerment and Child Protection carried out a national survey across 160 districts. The highest prevalence can be found on the island of Sulawesi (81.2% of all forms of sunat, and 50.9% of WHO FGC / unknown), followed by Kalimantan (73.1% of all forms of sunat and 44.3% of WHO FGC / unknown), Sumatra (69.7% of all forms of sunat and 43.7% of WHO FGC / unknown). The islands of Jawa / Bali, although home to over half the whole Indonesian population, record a national prevalence of sunat of 38.9% and 24.4% of WHO FGC / unknown).
The percentage of women who have heard the term FGM/C amounts to 86.9% in Sulawesi, 85.8% in Kalimantan, 79.6% in Sumatra and 63.4% in Java-Bali. In the rest of the country, only half the women have heard the term of FGM/C and 39.1% underwent a form of sunat.
In 2017 a survey was carried out a survey of the practice across the ten provinces which had recorded the highest prevalence in the 2013 national survey. Within these provinces prevalence ranged from 83.7% in Gorontalo (which recorded the highest rate at 93.1% in Bone Bolango District) to 60.4% in East Kalimantan. It is interesting to note that the latter, along with the next two with lowest prevalence, Jambi (69.7%) and West Nusa Tenggara (68.7), were the three provinces among the ten studied which have a legislative framework that supports the medicalization of FGM/C. In these districts perda (local regulations) exist that includes FGM/C as a part of health services and so generates a levy payable to the district government.
FGM/C Legislation in Indonesia
Government Regulation No.28/2024 (article 102(a)) banning female circumcisions for infants and children under the age of five was signed on 26 July 2024.
Development Indicators
Population Growth
279,476,346 with growth rate of 0.76 (2023 estimated). Ranks 4th in the world with 3.51% of global population.
Infant Mortality
19.3 deaths per 1000 live births, ranking 80 out of 227 countries (2023 estimated)
Maternal Mortality
173 deaths per 100,000 live births, ranking 52 out of 186 countries (2023 estimated)
SDG Gender Index
Score 70.2%, ranking 75 out of 166 countries (2023)